Science
Researchers Enhance Biofuel Supply Chain Resilience Amid Disruptions
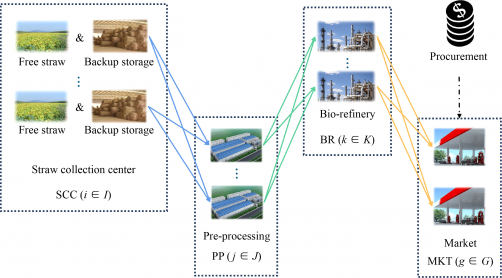
Researchers from Tianjin University have developed an innovative approach to enhance the resilience of biofuel supply chains in the face of disruptions. Their study, titled “Optimization design method for biofuel resilient supply chain considering node disruption impacts in a two-stage stochastic programming framework,” was published in the journal Frontiers of Chemical Science & Engineering, Volume 19, Issue 6.
As economic globalization progresses, biofuel supply chains are becoming more complex and extensive. This complexity introduces greater uncertainties and risks of disruptions for businesses operating within this sector. The need for resilient supply chains that can adapt to these challenges while ensuring security and competitiveness is increasingly pressing.
Traditional supply chain design methods often fall short in effectively addressing the risks associated with disruptions. Researchers identified a gap in the quantification and evaluation of these risks, prompting their investigation. To tackle this issue, the study proposes an improved Node Disruption Impact Index with adjustable parameters. This index assesses the cost changes in a supply chain resulting from disruptions at various nodes, allowing for the identification of nodes with differing risk levels and providing a means to evaluate the overall disruption impact.
Innovative Index and Optimization Model
The adjustable parameters within the Node Disruption Impact Index can be tailored to the specific needs of supply chain enterprises, enabling a balance between economic benefits and resilience. By applying this index to the fluctuation range of node uncertainties, the researchers developed a two-stage stochastic programming model aimed at optimizing supply chain operations while addressing potential high disruption risks.
The practical application of this model was tested on a biofuel supply chain case in Guangdong Province. The results revealed that in scenarios where high-risk nodes faced interruptions, the proposed optimization model significantly outperformed traditional models in terms of both cost efficiency and market delivery rates. This finding underscores the effectiveness of the new method in designing resilient supply chains.
The implications of this research extend beyond academic interest, as businesses increasingly seek strategies to navigate the complexities of global supply chains. The study not only provides a robust framework for assessing risks but also offers actionable insights for enhancing supply chain resilience.
For more detailed information, the full paper is available at: https://journal.hep.com.cn/fcse/EN/10.1007/s11705-025-2548-z.
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoLibraries Challenge Rising E-Book Costs Amid Growing Demand
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoTyreek Hill Responds to Tua Tagovailoa’s Comments on Team Dynamics
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoLiverpool Secures Agreement to Sign Young Striker Will Wright
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoSave Your Split Tomatoes: Expert Tips for Gardeners
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoPrincess Beatrice’s Daughter Athena Joins Siblings at London Parade
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoWinter Storms Lash New South Wales with Snow, Flood Risks
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoTrump Administration Moves to Repeal Key Climate Regulation
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoSoFi Technologies Shares Slip 2% Following Insider Stock Sale
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoSan Francisco Hosts Unique Contest to Identify “Performative Males”
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoNew Tool Reveals Link Between Horse Coat Condition and Parasites
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoElon Musk Sculpture Travels From Utah to Yosemite National Park
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoNew Study Confirms Humans Transported Stonehenge Bluestones









