Science
Mars 2020 Mission Unlocks Secrets of Jezero Crater’s Past
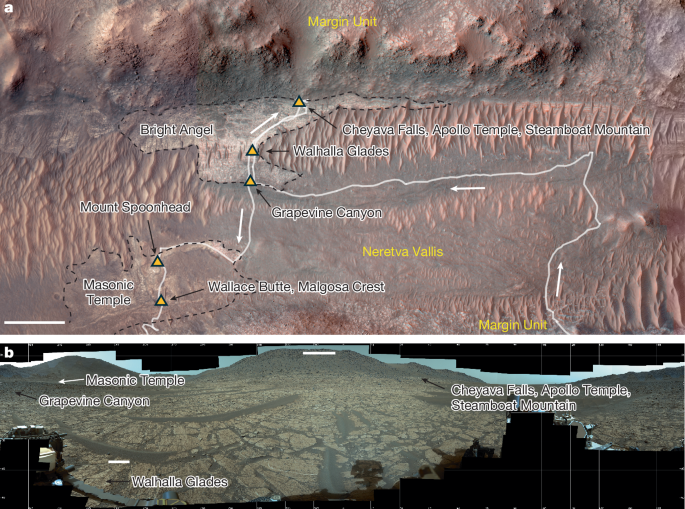
Recent findings from the Mars 2020 mission have revealed significant insights into the geological history of Jezero Crater, suggesting a dynamic past involving both mineral and organic associations. The Perseverance rover, which landed in February 2021, has been at the forefront of this exploration, collecting samples that may offer clues about ancient environments on Mars.
Understanding Jezero Crater’s Geological Significance
Jezero Crater is believed to have once housed a lake that was fed by an ancient river system, a feature that offers a unique opportunity to study Mars’ potential for past life. The rover’s team, led by researchers such as K. A. Farley, have documented the diverse sedimentary structures and mineralogy within the crater. Their work indicates that Jezero was not only a site for water accumulation but also a location where complex geological processes occurred.
In a study published in the journal *Science*, N. Mangold and colleagues highlighted the sedimentary fan deposits at Jezero, which reveal evidence of an ancient delta-lake system. This finding is crucial as it suggests that the area could have been habitable billions of years ago, providing a suitable environment for life.
The samples collected by the Perseverance rover have been meticulously analyzed. A recent article in the *Journal of Geophysical Research* by J. I. Simon and his team showcased the mineral diversity observed in the crater, emphasizing the presence of carbonates that could indicate past biological activity. These findings align with earlier research suggesting the ancient lake’s sediments might harbor organic materials.
Future Implications for Mars Exploration
The ongoing investigations at Jezero Crater are part of a larger effort to understand Mars’ habitability. Researchers anticipate that the data gathered from this mission could profoundly influence future missions and our understanding of planetary evolution. The exploration of Martian geology and potential biosignatures is critical for astrobiology, as detailed in a study led by K. A. Farley.
The Perseverance rover employs a suite of advanced instruments, including the Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman and Luminescence for Organics and Chemicals (SHERLOC) tool, to detect organic compounds and minerals. This technology enables scientists to analyze the planet’s surface composition in situ, providing invaluable data about the geochemical processes that have shaped Mars over time.
As the mission progresses, the findings from Jezero Crater will help paint a clearer picture of Mars’ past environments. With the potential discovery of ancient habitable conditions, the ongoing research may not only alter our understanding of Mars but also inform the search for life on other celestial bodies. The Mars 2020 mission continues to be a pivotal step in unraveling the mysteries of our neighboring planet.
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoLibraries Challenge Rising E-Book Costs Amid Growing Demand
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoTyreek Hill Responds to Tua Tagovailoa’s Comments on Team Dynamics
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoLiverpool Secures Agreement to Sign Young Striker Will Wright
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoSave Your Split Tomatoes: Expert Tips for Gardeners
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoPrincess Beatrice’s Daughter Athena Joins Siblings at London Parade
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoWinter Storms Lash New South Wales with Snow, Flood Risks
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoTrump Administration Moves to Repeal Key Climate Regulation
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoSan Francisco Hosts Unique Contest to Identify “Performative Males”
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoSoFi Technologies Shares Slip 2% Following Insider Stock Sale
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoNew Tool Reveals Link Between Horse Coat Condition and Parasites
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoElon Musk Sculpture Travels From Utah to Yosemite National Park
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoNew Study Confirms Humans Transported Stonehenge Bluestones









