Science
Cells Activate Emergency Defenses When Ribosomes Collide
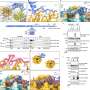
Recent research from the University of California, San Diego, has revealed that when ribosomes, the cellular machinery responsible for protein synthesis, collide, cells activate emergency stress defenses. This discovery sheds light on how cells maintain stability and function under stress, which is crucial for understanding various biological processes and diseases.
Ribosomes play a vital role in all living organisms by binding to messenger RNA (mRNA) and translating genetic information into proteins. They move along the mRNA strand, reading the genetic code and linking amino acids to form proteins. This process is essential for cell growth and repair. However, when ribosomes become overloaded or encounter obstacles, they can collide, leading to potential cellular dysfunction.
According to the study published in the journal Nature in April 2023, the collision of ribosomes triggers an immediate stress response within the cell. Researchers found that this response involves activating specific pathways that help the cell cope with the disruption. The study highlights that cells can rapidly switch from routine protein production to a defensive mode when faced with ribosomal collisions, thereby preserving cellular integrity.
The research team employed advanced imaging techniques to observe ribosomal behavior in real-time. They discovered that when ribosomes collide, the cell increases the production of certain stress response proteins. This adjustment allows the cell to manage the overload and restore normal function.
The implications of this research extend beyond basic biology. Understanding how cells respond to ribosomal collisions could provide new insights into diseases characterized by protein misfolding and aggregation, such as neurodegenerative disorders. As the study illustrates, ribosome collisions may contribute to cellular stress that underlies these diseases.
In addition, the findings could influence the development of therapeutic strategies aimed at enhancing cellular resilience in various conditions. Researchers believe that targeting the pathways activated during these stress responses may offer new avenues for treatment.
This groundbreaking study not only enhances our understanding of cellular mechanics but also underscores the importance of ribosomes in maintaining cellular health. As scientists continue to explore this area, the hope is to uncover further details that could lead to innovative approaches in combating diseases linked to protein synthesis and cellular stress.
In conclusion, the research from the University of California, San Diego, marks a significant advancement in our understanding of ribosomes and cellular stress responses. By revealing the emergency mechanisms activated during ribosomal collisions, this study lays the groundwork for future exploration in cell biology and its implications for health and disease.
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoLibraries Challenge Rising E-Book Costs Amid Growing Demand
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoTyreek Hill Responds to Tua Tagovailoa’s Comments on Team Dynamics
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoLiverpool Secures Agreement to Sign Young Striker Will Wright
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoSave Your Split Tomatoes: Expert Tips for Gardeners
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoPrincess Beatrice’s Daughter Athena Joins Siblings at London Parade
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoWinter Storms Lash New South Wales with Snow, Flood Risks
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoSan Francisco Hosts Unique Contest to Identify “Performative Males”
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoTrump Administration Moves to Repeal Key Climate Regulation
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoSoFi Technologies Shares Slip 2% Following Insider Stock Sale
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoNew Tool Reveals Link Between Horse Coat Condition and Parasites
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoElon Musk Sculpture Travels From Utah to Yosemite National Park
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoNew Study Confirms Humans Transported Stonehenge Bluestones









