Health
Experts Debunk Toilet Seat Myths: Risks and Realities Explained
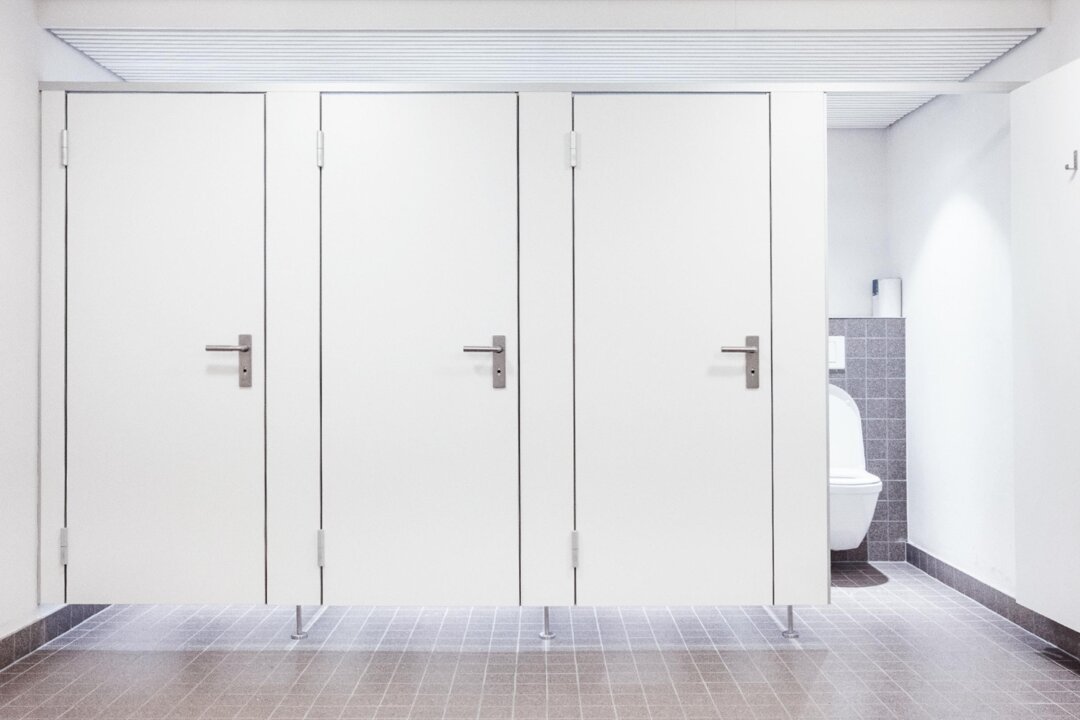

Concerns about germs on public toilet seats have long fueled anxiety among users. Many individuals believe that these surfaces are hotspots for dangerous pathogens, leading to fears of disease transmission. However, experts, including dermatologists and microbiologists, assert that while bathrooms can host various microorganisms, toilet seats are seldom the primary source of infection.
Dr. Chen Wei-di, a dermatologist based in Taiwan and a member of the American Academy of Dermatology, explained to The Epoch Times that although bacteria are present on toilet seats, most are benign or only pose a risk under specific conditions. This perspective is supported by a range of health professionals who emphasize that the most significant threats in restrooms come from other surfaces or the air itself.
Understanding Pathogens in Bathrooms
While the presence of harmful microorganisms is possible, the likelihood of contracting an infection from a toilet seat is minimal. Certain pathogens can survive in the bathroom environment, but the risk is more associated with surfaces that people frequently touch.
Dr. Huang Huilun, an attending physician at Ton-Yen General Hospital, highlighted that parasites like pubic lice and scabies, as well as common molds, can theoretically survive on toilet seats. These organisms can be transmitted to subsequent users, albeit infrequently.
In addition, research published in 2024 in Scientific Reports revealed that the bacterium Clostridium difficile can become aerosolized during flushing, posing a risk of colon inflammation. This underscores the importance of hygiene practices in bathroom environments.
The Real Risks: Airborne and Surface Pathogens
Gastrointestinal viruses such as norovirus predominantly attach to frequently touched surfaces, including flush handles, door knobs, and faucets. According to Dr. Chen, these viruses enter the human body primarily through hand contact with contaminated surfaces.
Furthermore, human waste can harbor E. coli and Salmonella, which can be dispersed in microscopic droplets when a toilet is flushed. These bacteria are known to spread through the fecal-oral route, leading to gastrointestinal illnesses, particularly diarrhea.
One of the most persistent fears surrounding public restrooms is the potential transmission of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) via toilet seats. Experts unanimously confirm that this concern is largely unfounded, as the likelihood of such transmission occurring in this manner is extraordinarily low.
In conclusion, while it is wise to maintain hygiene practices when using public restrooms, the notion that toilet seats are a major source of harmful pathogens is misleading. Understanding the realities of bathroom hygiene can alleviate unnecessary fears and promote healthier behaviors in public spaces.
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoLibraries Challenge Rising E-Book Costs Amid Growing Demand
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoTyreek Hill Responds to Tua Tagovailoa’s Comments on Team Dynamics
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoLiverpool Secures Agreement to Sign Young Striker Will Wright
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoSave Your Split Tomatoes: Expert Tips for Gardeners
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoPrincess Beatrice’s Daughter Athena Joins Siblings at London Parade
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoSan Francisco Hosts Unique Contest to Identify “Performative Males”
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoWinter Storms Lash New South Wales with Snow, Flood Risks
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoTrump Administration Moves to Repeal Key Climate Regulation
-

 Business5 months ago
Business5 months agoSoFi Technologies Shares Slip 2% Following Insider Stock Sale
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoNew Tool Reveals Link Between Horse Coat Condition and Parasites
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoElon Musk Sculpture Travels From Utah to Yosemite National Park
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoNew Study Confirms Humans Transported Stonehenge Bluestones