Science
Researchers Unveil Intricate Mechanism of Influenza Virus Infection
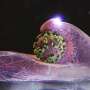
Research teams from Switzerland and Japan have made a significant breakthrough in understanding how influenza viruses infect living cells. In a groundbreaking study published in the journal Nature Communications, the scientists utilized advanced imaging techniques to observe the infection process in real time.
The study, conducted by experts from the University of Zurich and the University of Tokyo, revealed detailed interactions between the influenza virus and its host cells. The researchers noted that the virus enters the body through respiratory droplets, which then attach to cells lining the respiratory tract. Once attached, the virus employs a sophisticated mechanism to penetrate the cell membrane and begin its replication process.
Detailed Mechanism of Infection
Using state-of-the-art imaging technology, the researchers were able to visualize the entry of the influenza virus into cells, providing unprecedented insight into the viral life cycle. The team observed that the virus uses specific proteins to bind to the host cell’s surface, facilitating its entry. This detailed observation allowed the scientists to characterize the various stages of viral infection, from attachment to internalization.
According to the lead researcher from the University of Zurich, Dr. Maria Schmidt, this study offers crucial information on how influenza viruses adapt to their host environments. “Understanding the mechanics of viral entry could lead to the development of more effective antiviral therapies,” she stated. The research highlights the importance of targeting the initial stages of infection to inhibit the virus’s ability to replicate.
Implications for Future Research
The findings from this research not only deepen the scientific community’s understanding of influenza virus behavior but also pave the way for potential advancements in vaccine development and therapeutic strategies. By elucidating the precise mechanisms of infection, researchers hope to inform the creation of vaccines that can provide broader protection against various strains of the virus.
This study is particularly timely given the ongoing challenges posed by seasonal flu outbreaks and the potential for pandemic influenza strains. The researchers emphasize the need for continued investigation into the mechanisms of viral infection to better equip healthcare systems for future challenges.
The collaborative effort between Swiss and Japanese institutions underscores the global nature of scientific research, bringing together expertise and resources to tackle complex health issues. As influenza remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, these insights are critical in the ongoing fight against viral infections.
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoLibraries Challenge Rising E-Book Costs Amid Growing Demand
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoTyreek Hill Responds to Tua Tagovailoa’s Comments on Team Dynamics
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoLiverpool Secures Agreement to Sign Young Striker Will Wright
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoSave Your Split Tomatoes: Expert Tips for Gardeners
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoPrincess Beatrice’s Daughter Athena Joins Siblings at London Parade
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoSan Francisco Hosts Unique Contest to Identify “Performative Males”
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoWinter Storms Lash New South Wales with Snow, Flood Risks
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoTrump Administration Moves to Repeal Key Climate Regulation
-

 Business5 months ago
Business5 months agoSoFi Technologies Shares Slip 2% Following Insider Stock Sale
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoNew Tool Reveals Link Between Horse Coat Condition and Parasites
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoElon Musk Sculpture Travels From Utah to Yosemite National Park
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoNew Study Confirms Humans Transported Stonehenge Bluestones









