Science
Researchers Propose Serious Steps Toward Terraforming Mars
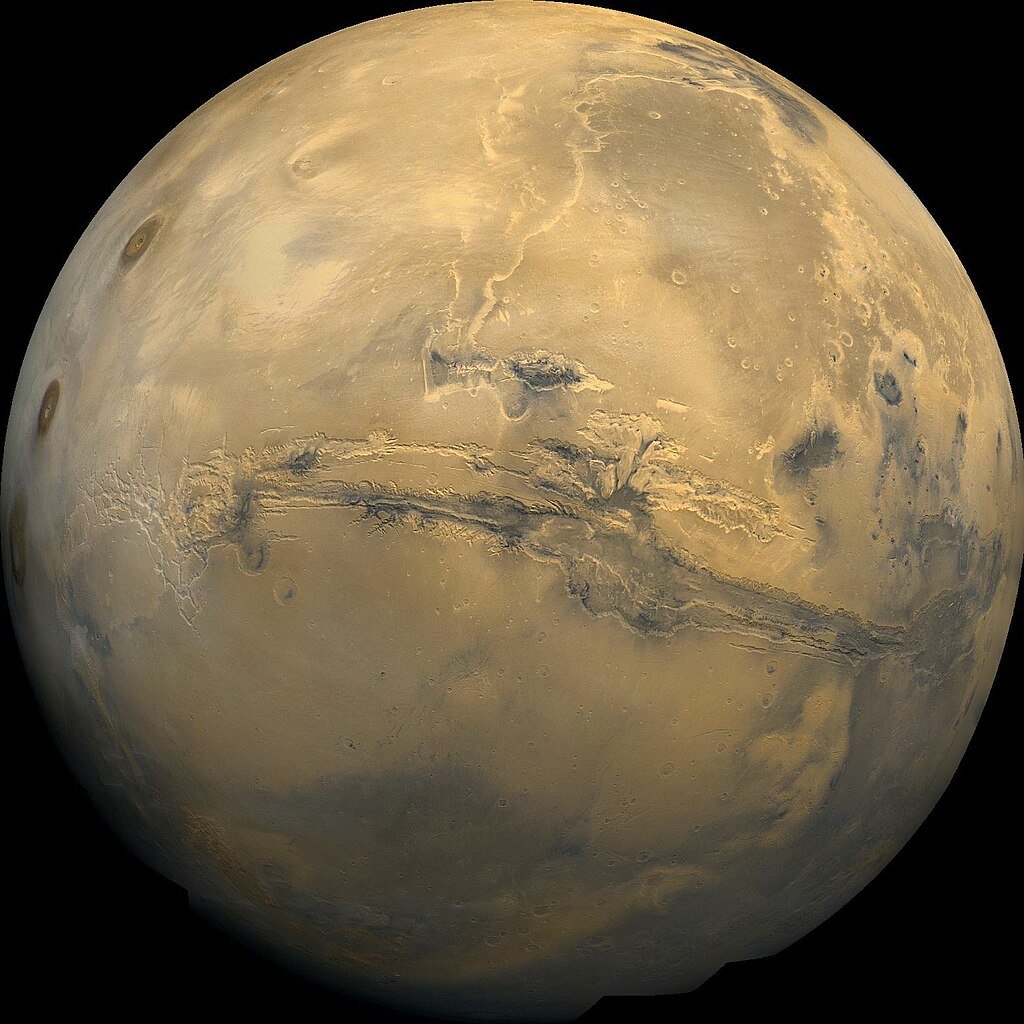
The concept of terraforming Mars has shifted from the realm of science fiction to a serious area of research. A team led by Dr. Erika DeBenedictis of Pioneer Labs argues that recent technological advancements warrant a reevaluation of how we approach transforming the Martian landscape into a habitable environment for humans and other Earth-like life forms. The findings were discussed in a workshop summary prepared for the upcoming 2025 Green Mars Workshop.
Terraforming involves altering a planet’s atmosphere, temperature, and surface conditions to mimic those of Earth. Proposals for Mars include increasing greenhouse gases to warm the planet and introducing engineered microorganisms that could gradually produce oxygen. Historically, this ambitious idea was dismissed by scientists as impossible. However, with breakthroughs in various scientific fields, the conversation has evolved.
Technological Advancements Shift Perspective
Dr. DeBenedictis emphasizes that 30 years ago, terraforming Mars seemed unfeasible. Today, technologies like SpaceX’s Starship, which may drastically reduce launch costs, combined with advances in synthetic biology and climate modeling, have changed the narrative. The focus is now on whether we should pursue terraforming and the steps required to achieve it.
The proposed plan unfolds in three phases. The first involves warming Mars by several degrees over a few decades using engineered aerosols or greenhouse gases. Recent studies indicate that Mars contains sufficient water ice to potentially create an ocean covering nearly four million square kilometers at depths reaching 300 meters. A temperature increase of approximately 30 degrees Celsius could initiate the melting of these frozen reserves, enabling liquid water to exist on the surface.
Establishing Life and Long-Term Goals
The second phase centers on introducing microbial life, where synthetic biology plays a crucial role. Researchers suggest engineering extremophiles—microbes that thrive in extreme conditions—to accelerate the terraforming process. These resilient organisms could cover Mars with algae-like growth within decades, initiating atmospheric transformation through photosynthesis.
The final phase extends over centuries or millennia, focusing on creating an oxygen-rich atmosphere capable of supporting complex life. The research team proposes starting with large domed habitats, around 100 meters tall, where photosynthesis and water electrolysis could generate breathable air. Over time, plant life would expand beyond these structures, contributing oxygen to the atmosphere.
Despite the ambitious nature of these proposals, significant unknowns remain. Questions linger about what exists beneath Mars’ extensive ice sheets, how dust storms would behave in a warmer environment, and whether the materials required for large-scale water electrolysis are plentiful on Mars or would necessitate costly imports from Earth.
Ethical Considerations and Earthly Benefits
The ethical implications of terraforming are also significant. Transforming Mars would alter its landscape in potentially irreversible ways. If indigenous Martian life exists, even at a microbial level, our interventions could eliminate it. The research team argues that understanding terraforming could provide immediate benefits for Earth, with technologies developed for Mars habitation potentially enhancing agricultural resilience and sustainability on our home planet.
Dr. DeBenedictis points out that while the workshop summary does not advocate for immediate terraforming missions, it calls for thorough laboratory studies, climate modeling, and small-scale experiments during future Mars missions. The goal is to explore localized warming strategies before considering a full-scale transformation of the planet.
The evolving discussion has transitioned from “could we?” to “should we, and if so, how?” This marks a significant step forward in the serious exploration of terraforming Mars, highlighting both the potential for groundbreaking advances and the need for careful consideration of the risks involved.
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoLibraries Challenge Rising E-Book Costs Amid Growing Demand
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoTyreek Hill Responds to Tua Tagovailoa’s Comments on Team Dynamics
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoLiverpool Secures Agreement to Sign Young Striker Will Wright
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoSave Your Split Tomatoes: Expert Tips for Gardeners
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoPrincess Beatrice’s Daughter Athena Joins Siblings at London Parade
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoSan Francisco Hosts Unique Contest to Identify “Performative Males”
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoWinter Storms Lash New South Wales with Snow, Flood Risks
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoTrump Administration Moves to Repeal Key Climate Regulation
-

 Business5 months ago
Business5 months agoSoFi Technologies Shares Slip 2% Following Insider Stock Sale
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoNew Tool Reveals Link Between Horse Coat Condition and Parasites
-

 Sports5 months ago
Sports5 months agoElon Musk Sculpture Travels From Utah to Yosemite National Park
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoNew Study Confirms Humans Transported Stonehenge Bluestones