Science
New Electrode Material Boosts Performance of Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
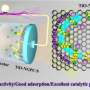
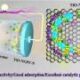
A research team led by Professor Jongsung Yu from the Department of Energy Science and Engineering at DGIST has developed a groundbreaking electrode material that significantly enhances the performance of lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries. The innovative approach allows for the simultaneous production of titanium monoxide (TiO) nanoparticles and nitrogen-containing honeycomb-structured highly graphitized porous carbon (TiO-NGPC) using a simple magnesium reduction process.
The advancement of Li-S battery technology is crucial as these batteries promise a higher energy density compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. The research team’s findings, published in a prominent scientific journal, indicate that the new composite material could lead to longer-lasting batteries with improved efficiency.
Innovative Production Process
The use of magnesium reduction in producing TiO and TiO-NGPC represents a significant shift in how these materials are synthesized. Traditionally, the production of such materials is complex and costly. This new method not only simplifies the process but also enhances the structural integrity of the materials involved.
The incorporation of TiO-NGPC within the battery electrodes allows for better conductivity and stability, which are critical factors in battery performance. According to the research, the new electrode material can potentially increase the lifespan of Li-S batteries significantly, making them more viable for commercial applications.
Implications for Battery Technology
The implications of this research extend beyond academic interest. The enhanced performance of lithium-sulfur batteries could pave the way for advancements in various industries, including electric vehicles and renewable energy storage. With global demands for efficient energy solutions rising, innovations like this one could play a pivotal role in meeting future energy needs.
As the technology matures, the team at DGIST aims to collaborate with industry partners to explore commercial applications of their discoveries. The potential for scalability and cost-effectiveness could make these batteries a popular choice in the market.
The study marks a significant step forward in battery technology, with Professor Yu emphasizing the importance of ongoing research to further refine these materials. As the quest for efficient energy storage solutions continues, this breakthrough offers promising prospects for the future of rechargeable batteries.
The research not only highlights the innovative spirit at DGIST but also underscores the importance of interdisciplinary approaches in solving complex energy challenges.
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoLibraries Challenge Rising E-Book Costs Amid Growing Demand
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoTyreek Hill Responds to Tua Tagovailoa’s Comments on Team Dynamics
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoLiverpool Secures Agreement to Sign Young Striker Will Wright
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoSave Your Split Tomatoes: Expert Tips for Gardeners
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoPrincess Beatrice’s Daughter Athena Joins Siblings at London Parade
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoSan Francisco Hosts Unique Contest to Identify “Performative Males”
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoWinter Storms Lash New South Wales with Snow, Flood Risks
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoTrump Administration Moves to Repeal Key Climate Regulation
-

 Business5 months ago
Business5 months agoSoFi Technologies Shares Slip 2% Following Insider Stock Sale
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoNew Tool Reveals Link Between Horse Coat Condition and Parasites
-

 Sports5 months ago
Sports5 months agoElon Musk Sculpture Travels From Utah to Yosemite National Park
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoNew Study Confirms Humans Transported Stonehenge Bluestones