Science
New Brain Activity Study Reveals Daily Patterns and Implications
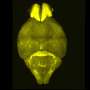
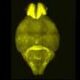
Research conducted by an international team led by the University of Michigan has unveiled new insights into how brain activity fluctuates throughout the day. Using innovative methods that allow for single-cell resolution, the study highlights which regions of the brain are active at various times, offering significant implications for understanding fatigue and mental health.
The findings, published on October 10, 2023, demonstrate that brain activity is not static but changes dynamically, reflecting different states of mental function and alertness. This research provides a clearer picture of the brain’s behavior across a typical day, revealing patterns that could inform approaches to managing fatigue and mental health conditions.
Innovative Techniques Unveiled
The research team employed cutting-edge techniques that enable the observation of neuronal activity at a granular level. By tracking the brain’s cellular responses throughout the day, they were able to identify specific areas of heightened activity. This method represents a significant advancement over previous techniques, which often provided a more generalized view of brain function.
Understanding the timing and intensity of brain activity could lead to targeted interventions for individuals experiencing chronic fatigue or mental health challenges. The study’s authors suggest that by recognizing these patterns, healthcare providers can better tailor treatments to align with the brain’s natural rhythms.
Implications for Mental Health and Fatigue
The implications of these findings extend beyond academic interest. They may inform strategies for improving mental health and addressing issues such as fatigue. As society grapples with increasing mental health challenges, understanding the underlying neural mechanisms is crucial.
The research indicates that certain brain regions may be more active during specific times, potentially correlating with optimal periods for cognitive tasks or relaxation. This insight could guide individuals in structuring their daily activities to align with their brain’s natural peaks and troughs.
In light of the growing recognition of mental health issues, these findings underscore the importance of a nuanced understanding of brain function. The research team plans to further investigate how these daily fluctuations impact overall well-being and cognitive performance.
The study not only sheds light on brain activity but also opens up new avenues for research. Future studies may explore how lifestyle factors, such as diet and exercise, interact with these brain patterns to influence mental health outcomes.
As the understanding of brain function continues to evolve, the findings from the University of Michigan research team could play a pivotal role in shaping future approaches to mental health care and enhancing quality of life for individuals worldwide.
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoLibraries Challenge Rising E-Book Costs Amid Growing Demand
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoTyreek Hill Responds to Tua Tagovailoa’s Comments on Team Dynamics
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoLiverpool Secures Agreement to Sign Young Striker Will Wright
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoSave Your Split Tomatoes: Expert Tips for Gardeners
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoPrincess Beatrice’s Daughter Athena Joins Siblings at London Parade
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoSan Francisco Hosts Unique Contest to Identify “Performative Males”
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoWinter Storms Lash New South Wales with Snow, Flood Risks
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoTrump Administration Moves to Repeal Key Climate Regulation
-

 Business5 months ago
Business5 months agoSoFi Technologies Shares Slip 2% Following Insider Stock Sale
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoNew Tool Reveals Link Between Horse Coat Condition and Parasites
-

 Sports5 months ago
Sports5 months agoElon Musk Sculpture Travels From Utah to Yosemite National Park
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoNew Study Confirms Humans Transported Stonehenge Bluestones