Science
NASA’s Asteroid Bennu Samples Reveal Life’s Building Blocks
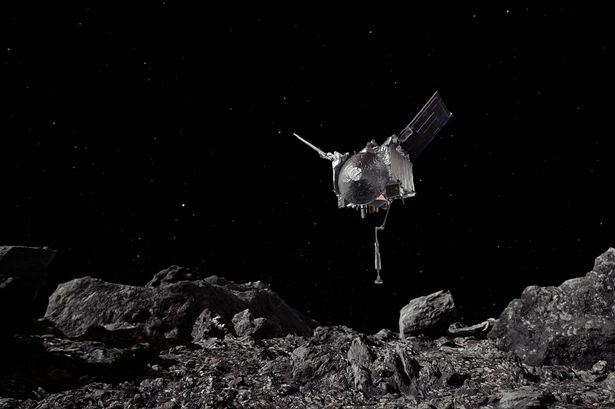

A recent analysis of samples retrieved from the asteroid Bennu has revealed significant discoveries that may reshape our understanding of life’s origins. The samples, brought back by a NASA spacecraft from approximately 63 million kilometers (or 39 million miles) away, contain essential components believed to be the building blocks of life.
Scientists have identified ancient water and an unusual substance described as “space gum,” which has never been seen before on an asteroid. These findings suggest that Bennu may have once been part of an ancient water world, providing a glimpse into the conditions that could foster life.
Groundbreaking Discoveries from Bennu
A team at Tohoku University in Japan made a groundbreaking discovery of sugars vital for life within the asteroid’s samples. This marks the first time such sugars have been found in an extraterrestrial sample. Alongside these sugars, scientists from NASA reported the presence of a flexible, gum-like material that does not exist elsewhere in our solar system.
Alexandra Doten, a space communications expert, shared these findings on TikTok, emphasizing their implications for our understanding of life’s origins. “They found some truly insane things,” she stated. “We already knew from this sample that the asteroid has high carbon content and water together—and together those indicate the building blocks for life as we know it.”
The analysis revealed that Bennu is rich in nitrogen and organic compounds, alongside a mineral called serpentine. This mineral bears a striking resemblance to rocks found in mid-ocean ridges on Earth, suggesting that Bennu might have originated from an environment similar to our planet’s oceans.
Implications for Life Beyond Earth
The research highlighted the discovery of 14 amino acids on Bennu, which are crucial for protein synthesis on Earth. Additionally, all five nucleotide bases that form DNA and RNA were found, along with sugars such as ribose and glucose. Ribose is essential for the structure of RNA, indicating that Bennu may contain all necessary components to form RNA.
“This has huge implications—it could imply that RNA is more prevalent in the universe and could be the dominant form of early life,” Doten explained. These findings challenge existing theories about life’s building blocks and their distribution across the cosmos.
In a separate study published in the journal Nature Astronomy, Scott Sandford from NASA’s Ames Research Center, along with Zack Gainsforth from the University of California, detailed the characteristics of the gum-like substance found on Bennu. NASA described it as a pliable material, likening it to used gum or soft plastic. Exposure to radiation made it brittle, akin to a lawn chair left out in the sun for too long.
Furthermore, a study led by Ann Nguyen from NASA’s Johnson Space Center revealed an unexpectedly high amount of dust produced by supernova explosions that predate our solar system, adding yet another layer of complexity to the findings from Bennu.
As researchers continue to unravel the mysteries of Bennu, these insights not only deepen our understanding of astrobiology but also open new avenues for exploring the potential for life beyond Earth. The discoveries underscore the importance of continued exploration and analysis of asteroids, which may hold the keys to understanding our own existence in the universe.
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoLibraries Challenge Rising E-Book Costs Amid Growing Demand
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoTyreek Hill Responds to Tua Tagovailoa’s Comments on Team Dynamics
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoLiverpool Secures Agreement to Sign Young Striker Will Wright
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoSave Your Split Tomatoes: Expert Tips for Gardeners
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoPrincess Beatrice’s Daughter Athena Joins Siblings at London Parade
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoSan Francisco Hosts Unique Contest to Identify “Performative Males”
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoWinter Storms Lash New South Wales with Snow, Flood Risks
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoTrump Administration Moves to Repeal Key Climate Regulation
-

 Business5 months ago
Business5 months agoSoFi Technologies Shares Slip 2% Following Insider Stock Sale
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoNew Tool Reveals Link Between Horse Coat Condition and Parasites
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoElon Musk Sculpture Travels From Utah to Yosemite National Park
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoNew Study Confirms Humans Transported Stonehenge Bluestones