Science
Revolutionary Magnetic Microcatheters Transform Reproductive Medicine
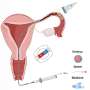
A groundbreaking international study led by the Nanobiosystems group at CIC nanoGUNE has unveiled innovative miniature, non-invasive robotic catheters designed for applications in reproductive medicine and gynecological health. This research aims to enhance the precision and effectiveness of medical interventions, potentially revolutionizing how healthcare providers approach treatments in this vital field.
The study focuses on developing magnetic microcatheters that can be maneuvered with high accuracy, facilitating targeted delivery of treatments while minimizing the risks associated with traditional invasive procedures. By harnessing advanced robotics and magnetic technology, these microcatheters promise to improve patient outcomes significantly.
Advancements in Medical Technology
The significance of this research lies in its potential to address critical challenges in reproductive medicine. Current methods often involve invasive surgical procedures that carry various risks, including infection and longer recovery times. The introduction of these robotic catheters could lead to less traumatic options for patients, allowing for quicker procedures and reduced hospital stays.
According to the team at CIC nanoGUNE, the microcatheters are designed to navigate through complex anatomical structures with ease. This technology enables healthcare professionals to deliver therapies directly to the affected areas, thereby increasing the efficacy of treatments. Moreover, the precise control offered by these devices minimizes damage to surrounding tissues, enhancing overall safety for patients.
The research team is optimistic about the impact of these innovations. “Our goal is to create tools that not only improve the accuracy of procedures but also enhance the overall experience for patients,” stated a representative from the Nanobiosystems group. This vision aligns with growing trends in healthcare that prioritize patient-centered care and technological integration.
Future Implications for Patient Care
As the study progresses, researchers are exploring various applications of these microcatheters beyond reproductive medicine. Potential uses could extend to other areas of gynecological health, offering a versatile tool for a range of medical conditions. The adaptability of this technology may also enable its application in different medical disciplines, further broadening its impact.
In terms of commercialization, the development of magnetic microcatheters could lead to significant advancements in the medical device industry. As healthcare providers increasingly seek less invasive solutions, the demand for such innovative technologies is likely to rise. This trend presents an opportunity for companies to invest in and develop similar technologies that can benefit patients worldwide.
In conclusion, the research spearheaded by the Nanobiosystems group at CIC nanoGUNE represents a promising step forward in the field of reproductive medicine. With its emphasis on precision and minimally invasive techniques, this study could pave the way for a new era in patient care, ultimately enhancing treatment outcomes and quality of life for countless individuals.
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoLibraries Challenge Rising E-Book Costs Amid Growing Demand
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoTyreek Hill Responds to Tua Tagovailoa’s Comments on Team Dynamics
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoLiverpool Secures Agreement to Sign Young Striker Will Wright
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoSave Your Split Tomatoes: Expert Tips for Gardeners
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoPrincess Beatrice’s Daughter Athena Joins Siblings at London Parade
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoSan Francisco Hosts Unique Contest to Identify “Performative Males”
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoWinter Storms Lash New South Wales with Snow, Flood Risks
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoTrump Administration Moves to Repeal Key Climate Regulation
-

 Business5 months ago
Business5 months agoSoFi Technologies Shares Slip 2% Following Insider Stock Sale
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoNew Tool Reveals Link Between Horse Coat Condition and Parasites
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoElon Musk Sculpture Travels From Utah to Yosemite National Park
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoNew Study Confirms Humans Transported Stonehenge Bluestones









