Top Stories
New Parkinson’s Drug Tolcapone Blocks Protein in Superbug Defense
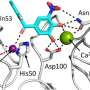
A study has revealed that the Parkinson’s drug tolcapone can inhibit a crucial protein involved in the infection process of the hospital superbug Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The research indicates that tolcapone blocks the sugar-binding protein LecA, which the pathogen uses to adhere to human cells and form biofilms, thereby complicating treatment.
Researchers from the Research Institute of the National University of Singapore conducted tests demonstrating that LecA plays a significant role in the development and progression of infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This pathogen is classified as a critical threat by the World Health Organization (WHO), particularly in hospital settings where it can lead to severe infections in patients, especially those with weakened immune systems.
The findings, published in October 2023, could have far-reaching implications for treating infections caused by this resistant bacterium. The ability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to form biofilms presents a major challenge in healthcare, as these biofilms protect the bacteria from both the immune system and antibiotic treatments. Consequently, infections can become chronic and difficult to eradicate.
LecA facilitates the initial attachment of the bacteria to tissues, marking a pivotal step in the infection process. By blocking this protein, tolcapone may offer a new approach to preventing or mitigating infections associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The potential repurposing of existing drugs like tolcapone underscores the significance of ongoing research into novel applications for established medications.
Dr. Tan Cheng Hock, a lead researcher on the study, stated, “Our results suggest that targeting LecA could significantly alter the course of infections caused by this superbug. This is an exciting development in the fight against antibiotic resistance.”
The emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria has become a pressing global health issue, prompting increased scrutiny and research into alternative treatments. The results of this study provide hope for new strategies to combat superbugs, especially in vulnerable populations.
Further investigation is needed to determine the effectiveness of tolcapone in clinical settings, but the initial findings present a promising avenue for enhancing treatment options against one of the most threatening pathogens identified by health authorities worldwide. As the healthcare community continues to grapple with the challenges posed by antibiotic resistance, such innovative approaches could prove invaluable in safeguarding patient health.
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoLibraries Challenge Rising E-Book Costs Amid Growing Demand
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoTyreek Hill Responds to Tua Tagovailoa’s Comments on Team Dynamics
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoLiverpool Secures Agreement to Sign Young Striker Will Wright
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoSave Your Split Tomatoes: Expert Tips for Gardeners
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoPrincess Beatrice’s Daughter Athena Joins Siblings at London Parade
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoWinter Storms Lash New South Wales with Snow, Flood Risks
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoSan Francisco Hosts Unique Contest to Identify “Performative Males”
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoTrump Administration Moves to Repeal Key Climate Regulation
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoSoFi Technologies Shares Slip 2% Following Insider Stock Sale
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoNew Tool Reveals Link Between Horse Coat Condition and Parasites
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoElon Musk Sculpture Travels From Utah to Yosemite National Park
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoNew Study Confirms Humans Transported Stonehenge Bluestones









