Science
Massive 900-Metre Crater Discovered in Guangdong, China
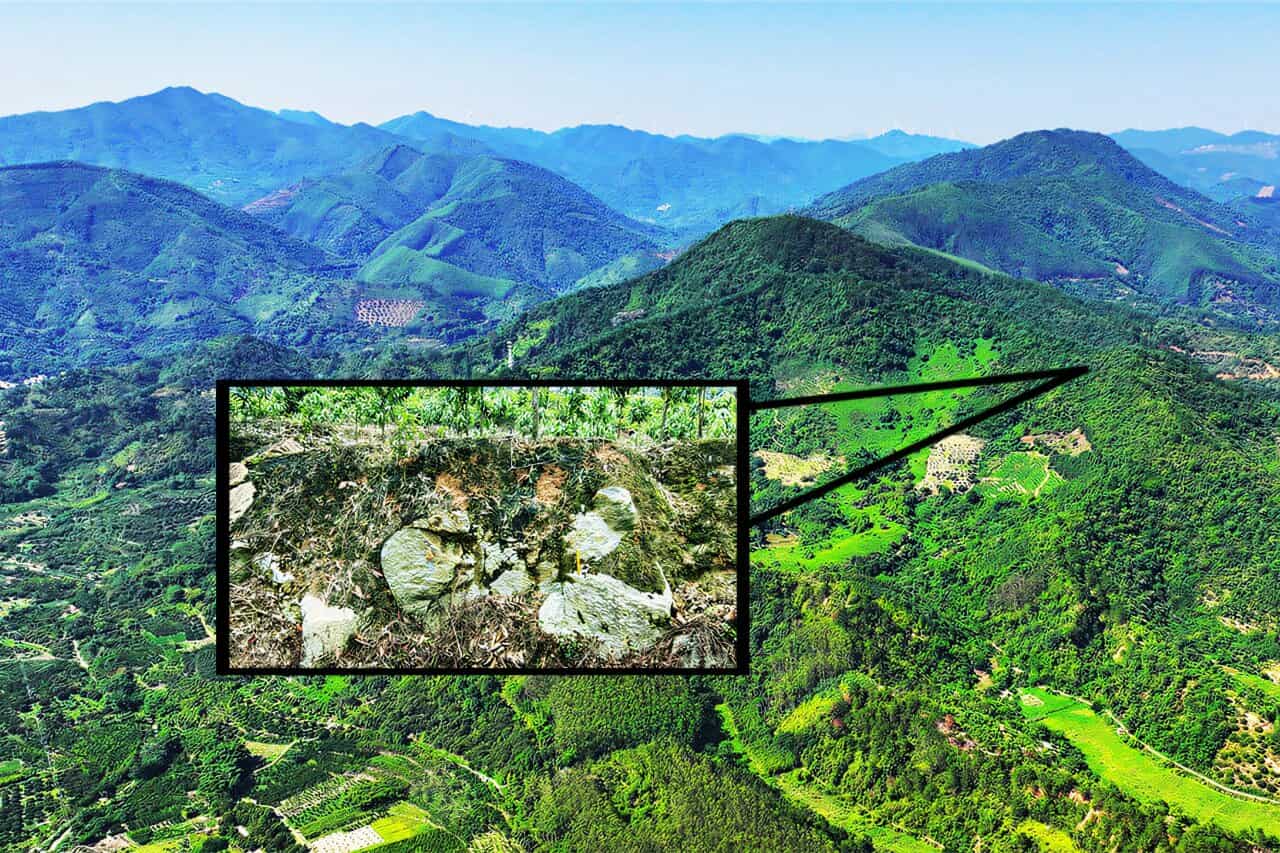

Researchers have unveiled the Jinlin crater, a remarkable impact structure located on a hillside in Guangdong Province, near Zhaoqing City, China. This newly identified crater, measuring between 820 and 900 metres in diameter and reaching a depth of 90 metres, is not only significant due to its size but also because of its relatively young age, having formed during the Holocene epoch approximately 11,700 years ago.
The discovery of the Jinlin crater is particularly noteworthy, as it adds to the limited number of confirmed impact craters worldwide, currently estimated at around 200. Prior to this finding, the largest known impact structure from the Holocene was Russia’s 300-metre Macha crater. Researchers believe that the Jinlin crater was created during the early to mid-Holocene, as indicated by soil erosion measurements in the surrounding area.
Surprising Preservation Despite Climate Challenges
The existence of such a large and well-preserved crater is unexpected, given the climatic conditions of the region. Guangdong Province is known for its regular monsoons, heavy rainfall, and high humidity—conditions that typically accelerate erosion and could have obliterated any visible crater over time. Remarkably, the Jinlin crater remains intact, shielded by thick layers of weathered granite that have protected its structure from erosive forces.
The crater’s extraterrestrial origin is supported by specific geological features found within the granite. Researchers discovered numerous quartz fragments displaying planar deformation features, which are microscopic characteristics indicative of impact events. These features arise under extreme pressure conditions, ranging from 10 to 35 gigapascals, levels that far exceed those produced by Earth’s geological processes. Such intense shockwaves are solely the result of hypervelocity collisions with extraterrestrial objects.
While researchers have confirmed that the impactor was a meteorite rather than a comet—given that a comet would have created a crater at least 10 kilometres wide—they have yet to determine the composition of the meteorite, whether it is iron or stone. Significant work remains to fully understand the implications of this discovery.
Implications for Impact History
The Jinlin crater challenges existing assumptions about the frequency and scale of recent impacts on Earth. The planet’s surface is theoretically subject to equal bombardment from space debris, yet geological variations result in different rates of erosion for impact evidence. As a result, some craters may vanish entirely, while others, like Jinlin, endure. This uneven preservation skews our understanding of Earth’s impact history.
Interestingly, confirmed craters often cluster in regions with well-funded geological research programs. The discovery of the Jinlin crater in a remote, forested area suggests that many more impact structures could remain unidentified in less-studied locations.
As ongoing research continues at the Jinlin crater, it has the potential to provide new insights into the frequency of significant impacts on our planet. Additionally, it may inform scientists about what factors contribute to the preservation or destruction of the evidence left behind by these cosmic events.
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoLibraries Challenge Rising E-Book Costs Amid Growing Demand
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoTyreek Hill Responds to Tua Tagovailoa’s Comments on Team Dynamics
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoLiverpool Secures Agreement to Sign Young Striker Will Wright
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoSave Your Split Tomatoes: Expert Tips for Gardeners
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoPrincess Beatrice’s Daughter Athena Joins Siblings at London Parade
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoWinter Storms Lash New South Wales with Snow, Flood Risks
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoTrump Administration Moves to Repeal Key Climate Regulation
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoSan Francisco Hosts Unique Contest to Identify “Performative Males”
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoSoFi Technologies Shares Slip 2% Following Insider Stock Sale
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoNew Tool Reveals Link Between Horse Coat Condition and Parasites
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoElon Musk Sculpture Travels From Utah to Yosemite National Park
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoNew Study Confirms Humans Transported Stonehenge Bluestones